How does photovoltaics work?

The basic principle of solar power generation
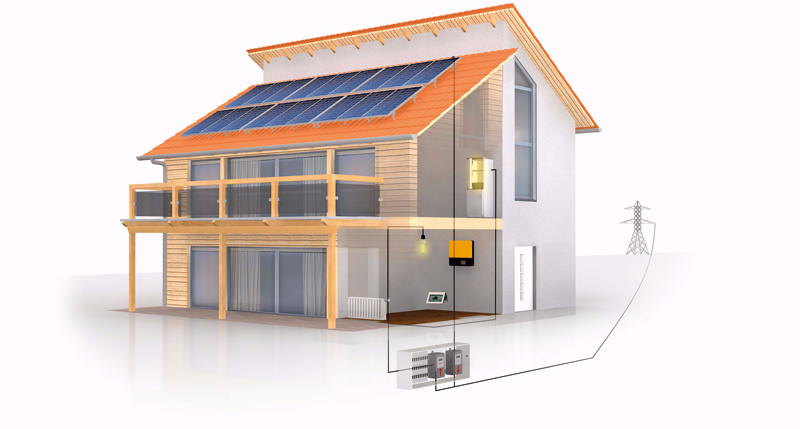
The basic principle of a photovoltaic system is the conversion of sunlight into electricity – by means of solar cells.
The main component of most solar cells is silicon. The element, which is very common in nature, is refined into high grade wafers for solar cells in special high-tech industrial processes.
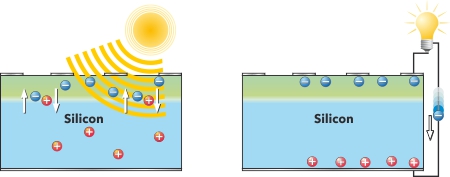
If the sun shines onto the solar cells, the photo-effect, originally discovered by Albert Einstein, induces a DC voltage between the top and bottom, and electricity begins to flow. Commercially available solar cells today achieve an efficiency of up to 20% and are combined into solar modules of varying sizes.
The electrical energy, which is generated as direct current (DC), is converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter (usually part of a grid feeder) and thus the solar power can be fed into the public power grid, used for own consumption or temporarily stored in batteries for later use.
Autonomous off-grid systems – also called "island systems“ – are the technology of choice for vacation homes, remote regions or special technological solutions that must function without grid access. Island systems do not feed the generated solar power into a grid at all, but instead for example supply small consumers and appliances in the house (lighting, light, cooling, pumps, etc.) directly from a battery.
How does a grid-connected system work?
The simplest way to use the electricity generated by a solar power system is to feed it into the grid. In many countries a national feed-in-tariff (FIT) guarantees an attractive remuneration for private and commercial producers of solar power, usually through arrangements with the local utility companies or grid operators. Your Wagner Solar partner will also be happy to provide you with more information about your respective local opportunities.
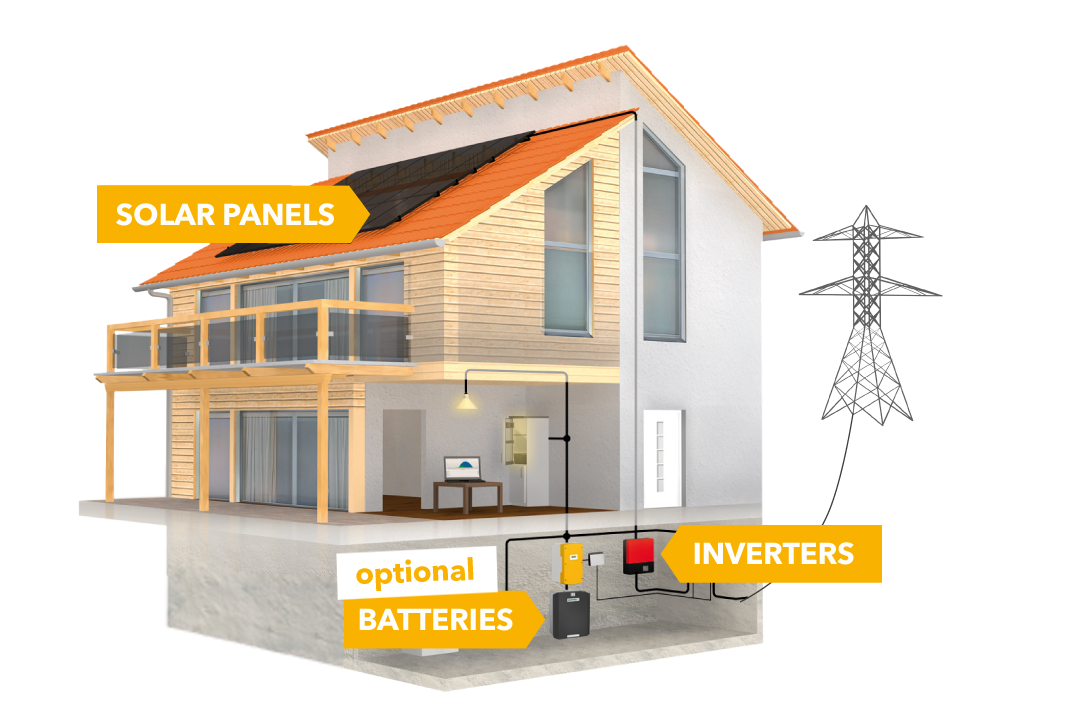
Our solar modules convert the radiation energy coming from the sun to electric energy. The resulting DC power has to be converted to standard household AC power. This is the job of our inverters. Additionally, our solar power storage batteries allow you to conveniently store the electricity for later use.
How do autonomous systems work?
Autonomous so-called "island systems" are suitable for holiday homes, off-grid regions and special off-grid applications, such as weather stations and many more. They do not feed solar power into the grid but supply it to small consumers in either directly or from a battery (household appliances such as lighting, light, cooling, pumps, or measuring instruments etc.).
How a DC-coupled system works:
The excess energy generated by the solar modules and not consumed during daytime is stored in a battery bank to ensure its availability at night or during bad weather. Special charge controllers protect the batteries against damage from overcharging or deep discharge. A connected inverter can also enable the operation of standard 230 V loads.

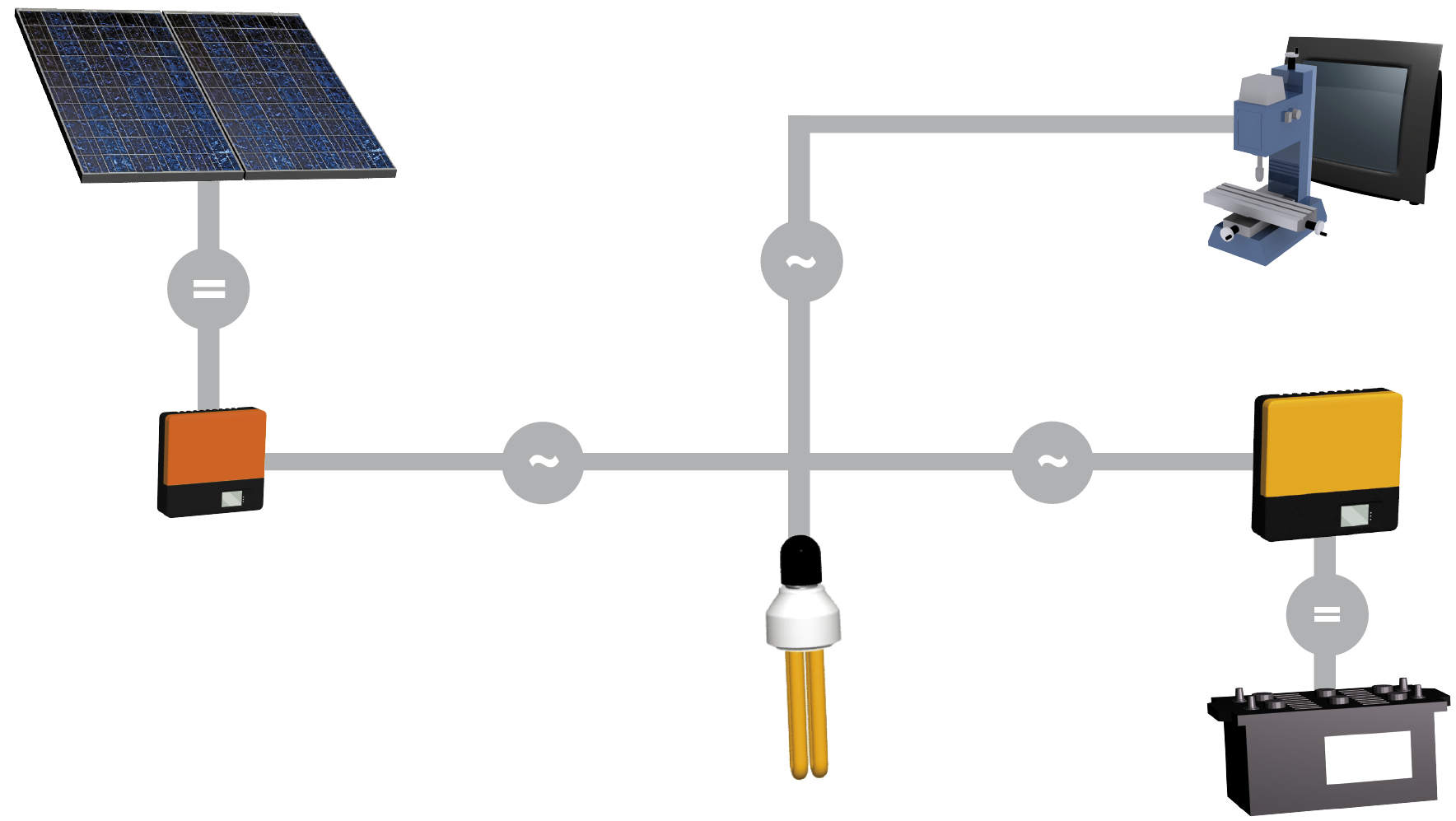
How an AC-coupled system works:
The solar modules feed the electricity directly into an autonomous 230V island grid via a Sunny Boy grid feeder. Excess power is stored in solar batteries by means of the bidirectional Sunny Island battery inverter and can be called up upon demand at any time required. The battery inverter simultaneously controls the Sunny Boy grid feeder.
How do solar thermal systems (solar heat) differ from photovoltaic systems (solar electricity)?
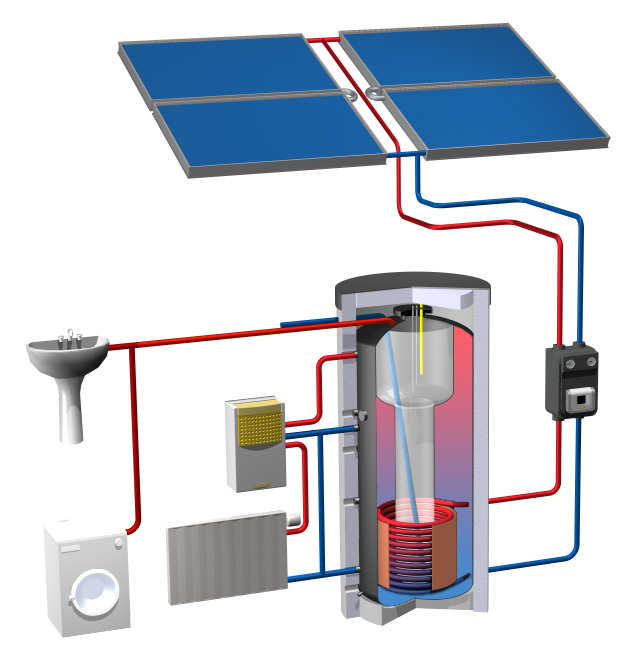
Solar thermal systems (solar heat) are based upon usually roof mounted solar collectors that generate heat by converting short wave solar radiation to thermal energy for space heating or hot water production. With conversion efficiencies of up to almost 98%, solar thermal systems are by far the most efficient method to utilize solar energy to, for example, significantly reduce oil or gas consumption in homes and industrial settings.
Inphotovoltaic systems(solar power), solar modules, also called PV (photovoltaic) modules, generate electricity from sunlight.
This solar power can be used for own consumption and thus reduces your own electricity bill. It can also be fed into the public grid for a fee – or both. More and more solar collectors are installed on roofs in combination with PV as hybrid systems, because these days this dual utilization is the most reasonable and economic way to harvest the sun’s free energy.
If you want to use as much as possible of your generated solar power for yourself, you can achieve this with modern solar power storage batteries. The excess solar electricity is temporarily stored in batteries and can thus be used independently of weather and time of day.

Is my house suitable for a photovoltaic installation?
Today, a roof area of about 24 to 40 m² typically is required for a photovoltaic system on a detached single-family home. The conditions are ideal, if the roof surface faces southeast to southwest and is inclined between 15° and approx. 60° (northern hemisphere).
How large should a photovoltaic system be?
Today we typically recommend sizes from 3 to 6 kWp (kilo Watt peak) for a photovoltaic system for a single-family house. This corresponds to about 24 to 40 m² of roof area.
How much energy does a photovoltaic system produce?
Depending on the location and orientation of the installed solar modules, annual electricity yields of between 900 and 1100 kWh per kWp are a typical range for Western Europe. A radiation atlas provides more precise information. Ask your Wagner partner for a yield estimate at your location!
Does the solar power have to be fed into the grid?
Not necessarily. Most generated solar power is usually fed into the grid. However, your system is more profitable if you use as much of your own electricity as possible yourself. This can be approx. 25 to 30 % of the solar power production without further technical aids (e.g. batteries).
If an intelligent battery system is added, internal consumption rates of up to 70 % are possible for typical households!
Where can solar modules be mounted?
With suitable mounting systems, solar modules can be securely set up on sloping and flat roofs just as well as at facades or on the ground as greenfield installations
How long is the service life of a photovoltaic system?
A photovoltaic system is designed for a service life of 30 years and more. The manufacturers of the solar modules offer a 25-year performance guarantee and a 10-year product warranty.
Does a photovoltaic system require a building permit?
As a rule, a building permit is not required. However, there are exceptions depending on respective local, regional and country regulations. In Germany, for example, special permits are required for installation on buildings listed as historic monuments and building permits are required for larger greenfield installations. Please contact your local Wagner partner and/or your local building authorities for details regarding your respective regulations.
Is the purchase of a new photovoltaic system still worthwhile?
Over the past years, the prices of solar power systems have fallen dramatically. Hardly any other technology has seen such an enormous cost reduction. Investing in a photovoltaic system therefore clearly is worthwhile in any case, despite reduced feed-in tariffs. Besides that, solar power now already is cheaper than grid-based household electricity from most electricity provider. Hence even it is increasingly worthwhile to utilize the generated solar power yourself!
Will new photovoltaic systems increase the price of electricity?
The answer depends on the respective national regulations and energy policies. In Germany the further expansion of solar power by now hardly contributes to the increase in the EEG (energy feed-in law) levy and consumer electricity prices at all. One gigawatt (GW) of newly installed solar power capacity in 2014 only increases the EEG levy for households by 0.019 ct/kWh.
What contribution do photovoltaic systems make to the power production mix today?
In Germany, to stay with the example of the country we are based in, solar power systems account for 6.1% of gross electricity generation Germany in 2017, corresponding to around 43 GW of installed generation capacity, while in the United Kingdom just over 3% of electricity are solar.
(Sources: International Energy Agency, Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Research, German Federal Statistics Office, retrieved 03/2018)
Recycling of Solar PV Modules

Solar modules provide clean electricity for at least 25 years. However, as a responsible company you have to think beyond this time from the beginning. The European WEEE directive (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) stipulates that solar modules – like all other decommissioned electrical equipment ¬– must not be disposed of with household waste, but rather has to be recycled in an environmentally friendly manner.
Consumers can return their old modules free of charge and in typical quantities to their respective municipal collection points. Recycling of old solar modules recovers highly valuable raw materials and thus reduces the need for primary raw materials and the related environmental damage.



